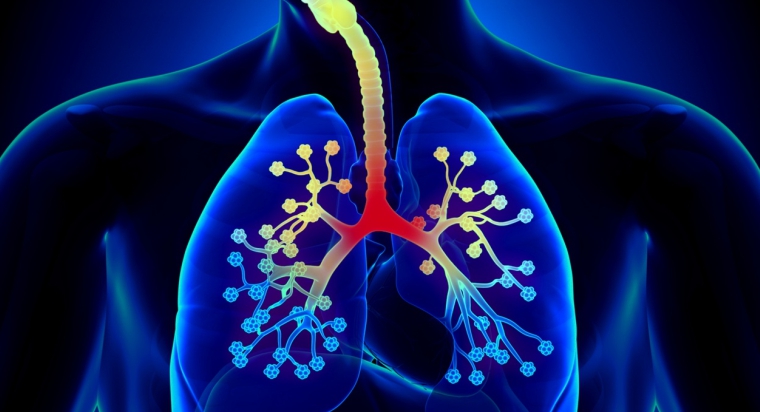
What is bronchitis?
Bronchitis is inflammation of the lining tubes (called Bronchial tubes) that carry air to and from the lungs which cause discomfort during breathing.
Are there types of bronchitis?
Yes. They are grouped into two: Acute and Chronic bronchitis.
- Acute Bronchitis: Acute bronchitis lasts for a few days (about five to ten days). It can be referred to as short-term bronchitis.
- Chronic Bronchitis: This is a kind of bronchitis that lasts for months, and keeps getting worse. When the bronchial tubes get continuously irritated and inflamed, it causes long-term bronchitis.
Do bacteria and viruses cause bronchitis?
Yes. Most cases of acute bronchitis are caused by viral infections from the air, either from the spread of viruses and bacteria or from fumes and dust. They’re not much to worry about; they’re short-term.
What are the causes of chronic bronchitis?
Based on statistics, most people who get diagnosed with chronic bronchitis have some history with tobacco. Since frequent tobacco abusers are most likely to have chronic bronchitis, we could say that’s a cause for it.
Is bronchitis contagious?
Bronchitis is usually diagnosed in people whose airways are inflamed, those who show long periods of coughing, and those whose production of mucus becomes excessive. It is contagious only if the source of infection is bacteria and viruses. Then, it can easily be contracted by the inhalation of cough particles from an infected person. It is not contagious if the source of infection is smoking, seeing as the airways were not infected by bacteria of any kind.
How do I know if I’m infected?
The following is a list of regular symptoms that those infected with bronchitis will experience:
- Constant coughs
- Excessive production of mucus
- Muscle aches
- Fever
- Fatigue
If you experience three or more of the above symptoms, you should see a lung doctor as soon as possible.
How is Bronchitis diagnosed?
Acute bronchitis is usually diagnosed by the doctor after asking about your cough and infection history. If you start getting symptoms after exposure to a certain environmental condition and it matches that which breeds infectious bacteria, you can be diagnosed as infected with bronchitis.
Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, doesn’t get diagnosed so easily. Several steps would be taken to rule out the possibility of other infections or diseases. So, after your doctor asks about your lung history and does a physical test, he might deem it necessary for you to have a Pulmonary function testing; An X-ray of the chest region to check for other possible causes of your symptoms; a sputum sample test; and probably a CT scan of the chest region.
How do I prevent being infected?
Preventive measures cannot be hundred percent effective, but you can try to avoid the risk of infection by:
- Not smoking
- Avoiding places where people smoke
- Avoid places with atmospheres that irritate your airways (like factories).
- Being on a healthy diet
- Washing your hands regularly
- Paying regular visits to a pulmonologist
Why see a Pulmonologist?
Seeing a pulmonologist regularly, aside from actions you take to evade the disease, will ensure your mind is at peace. Regular assessment of your lungs will help you discover any irregularities early.
Conclusion
When taken for granted, bronchitis can get fatal, so don’t hesitate to reach out to a lung doctor if you feel any symptoms of bronchitis or if you notice little changes after visiting a hospital. You can also contact us at ANY time to connect with an efficient lung doctor or make more inquiries about your pulmonary health.


 Translate
Translate