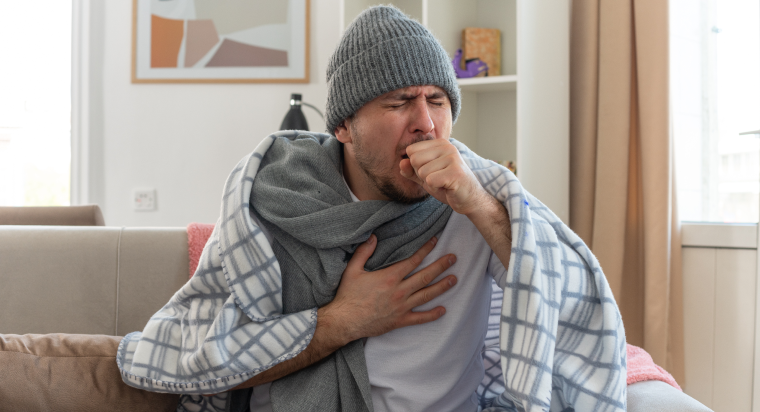
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and can range from mild to life-threatening. If you’re concerned you might have pneumonia, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Here are some answers to frequently asked questions about this condition.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the cause and your overall health. Common signs include:
- Cough (may produce mucus)
- Fever and chills
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain, especially when taking a deep breath or coughing
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Wheezing
Who is at risk for pneumonia?
Apart from the question, what are the symptoms of pneumonia, this is another commonly asked question. Anyone can get pneumonia, but certain groups are at higher risk, including:
- Infants and young children
- Adults over 65
- Individuals with chronic health conditions like asthma, heart disease, or diabetes
- Smokers
- People who have recently had a cold or the flu
How is pneumonia diagnosed?
So, how is pneumonia diagnosed? Well, diagnosis of pneumonia often involves a combination of:
- Physical examination: Your doctor will listen to your lungs for abnormal sounds.
- Chest X-ray: This imaging test can show areas of infection in your lungs.
- Sputum test: A sample of mucus coughed up from the lungs is analyzed to identify the cause of infection.
- Blood tests: These may be done to check for white blood cell count, which can indicate infection.
How is pneumonia treated?
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the type and severity of the infection. Common treatments include:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the bacteria.
- Antivirals: For viral pneumonia, antiviral medications may be used to shorten the illness.
- Cough suppressants: These can help ease a persistent cough.
- Pain relievers: Medications can help manage fever and chest pain.
- Oxygen therapy: In severe cases, additional oxygen may be needed to support breathing.
How long does it take to recover from pneumonia?
Most people with mild pneumonia recover within one to two weeks with proper treatment. However, recovery can take longer for individuals with underlying health conditions or severe cases.
Can pneumonia be prevented?
Several steps can help you reduce your risk of developing pneumonia:
- Get vaccinated: The pneumococcal vaccine and the flu shot can help prevent specific types of pneumonia and influenza, which can sometimes lead to pneumonia.
- Practice good hand hygiene: Washing your hands frequently can help prevent the spread of germs that can cause pneumonia.
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brushing and flossing regularly help reduce bacteria in your mouth, which can potentially travel to your lungs.
- Don’t smoke: Smoking damages your lungs and increases your risk of infections like pneumonia.
- Manage chronic health conditions: Keeping underlying health issues under control can reduce your susceptibility to pneumonia.
When should I seek medical attention for pneumonia?
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek immediate medical attention:
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing
- High fever (over 102°F)
- Confusion or sudden mental changes
- Coughing up blood
Is pneumonia contagious?
Some types of pneumonia, particularly those caused by bacteria or viruses, can be contagious through coughing, sneezing, or close contact with an infected individual.
What are the potential complications of pneumonia?
Having properly answered the questions like what are the symptoms of pneumonia, how pneumonia is diagnosed, and when to seek help for the condition, it is important to address another commonly asked question – the criticality of pneumonia.
In rare cases, pneumonia can lead to serious complications, including:
- Pleural effusion (fluid buildup around the lungs)
- Lung abscess (collection of pus in the lung)
- Bloodstream infection (bacteria entering the bloodstream)
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS, severe breathing difficulty)
Final Words
If you have concerns about pneumonia or any other lung-related issue, the Pulmonary Clinic of the Carolinas is here to help. We offer comprehensive diagnostic services, advanced treatment options, and compassionate care to ensure your lung health and well-being.
Schedule an appointment today to discuss your concerns and get the personalized care you deserve.


 Translate
Translate