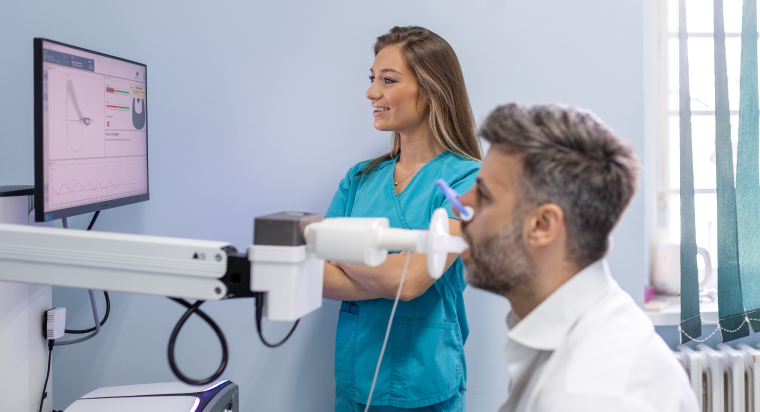
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) are a crucial tool in diagnosing and managing various respiratory conditions. These non-invasive tests provide valuable insights into a patient’s lung function and play a pivotal role in the practice of respiratory medicine. What are pulmonary function tests? What are the benefits of pulmonary function tests? How significant are PFTs in patient care? We’ll explore all these and more in this article. Read on!
What are Pulmonary Function Tests?
Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs) are a series of non-invasive tests that evaluate the functioning of a person’s lungs. These tests measure essential parameters such as lung capacity, airflow, and gas exchange efficiency, providing valuable insights into a patient’s respiratory health.
Pulmonary function tests are instrumental in diagnosing and managing respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung diseases, and cystic fibrosis. They help healthcare professionals design personalized treatment plans, monitor disease progression, and assess lung function before major surgeries. Early detection through PFTs enables timely intervention, leading to better outcomes and improved overall lung health.
The three most common types of PFTs include:
1. Spirometry: Assessing Airflow
Spirometry is the most fundamental PFT, evaluating lung function by measuring the amount of air inhaled and exhaled and the rate of airflow. During the test, the patient takes a deep breath and then forcefully exhales into a mouthpiece connected to a spirometer. Spirometry helps in diagnosing conditions like asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and interstitial lung diseases. It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments such as bronchodilators.
2. Lung Volume Tests: Understanding Lung Capacity
Lung volume tests, or lung volume testing, help in determining the total capacity of the lungs and the distribution of air within them. These tests are crucial in diagnosing restrictive lung diseases, which affect lung expansion and lead to reduced lung volumes. One of the common lung volume tests is the plethysmography test, where the patient sits inside a sealed booth and breathes into a mouthpiece. Lung volume tests are also valuable in understanding the extent of lung damage caused by various conditions and can be used to monitor disease progression over time.
3. Diffusion Capacity Tests: Evaluating Gas Exchange
Diffusion capacity tests measure how efficiently oxygen is absorbed from the lungs into the bloodstream and how well carbon dioxide is eliminated. In this test, the patient breathes in a small quantity of carbon monoxide, which is harmless, and then exhales it. By measuring the difference in the concentration of carbon monoxide in the inhaled and exhaled air, the diffusion capacity is calculated. These tests are particularly useful in diagnosing conditions affecting the alveoli, the tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs, such as pulmonary fibrosis and interstitial lung diseases.
Benefits of Pulmonary Function Tests
PFTs are critical in patient care in several ways. Some of them include:
1. Early Diagnosis and Intervention
One of the foremost benefits of pulmonary function tests is their ability to detect lung abnormalities even before symptoms become apparent. Early detection enables timely intervention, leading to better outcomes and preventing further deterioration in lung function. For conditions like asthma, early diagnosis allows for prompt treatment and better management, reducing the risk of exacerbations and hospitalizations.
2. Customized Treatment Plans
PFTs provide detailed information about a patient’s lung function, allowing healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans to their specific needs. By understanding the severity of a patient’s lung disease, doctors can prescribe appropriate medications, recommend lifestyle changes, and design personalized rehabilitation programs. This personalized approach improves patient compliance and overall health, leading to better long-term outcomes.
3. Monitoring Disease Progression
For patients with chronic respiratory conditions, regular PFTs offer a valuable means of monitoring disease progression. Tracking changes in lung function over time helps healthcare providers assess treatment effectiveness and make adjustments as necessary. For example, in COPD patients, periodic PFTs help in evaluating the rate of decline in lung function and adjusting medication dosages or initiating oxygen therapy when required.
4. Surgical Evaluation
Before major surgeries, especially those involving the respiratory system, PFTs can help assess a patient’s lung function and identify potential risks. This pre-operative evaluation ensures safer outcomes and helps healthcare providers make informed decisions regarding the surgery’s timing and the patient’s post-operative care plan.
The Role of PFTs in Common Respiratory Conditions
Asthma
PFTs play a critical role in diagnosing asthma and determining its severity. The spirometry component of PFTs helps identify airflow obstruction, and the results can be used to establish an asthma diagnosis. Additionally, spirometry is used in monitoring asthma control and guiding the appropriate use of bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate symptoms.
COPD
In patients with COPD, PFTs help differentiate between chronic bronchitis and emphysema and quantify the degree of lung damage. Spirometry is used to assess airflow limitation, and lung volume tests help determine the presence of hyperinflation and reduced lung volumes. This information guides treatment choices, such as pulmonary rehabilitation, long-term oxygen therapy, and the use of bronchodilators and corticosteroids.
Interstitial Lung Diseases
PFTs are essential in diagnosing and monitoring interstitial lung diseases, such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Lung volume tests and diffusion capacity tests provide vital data on lung function and gas exchange efficiency, helping to evaluate disease progression and response to therapy. Early detection and monitoring of IPF through PFTs can lead to timely interventions and improved quality of life for patients.
Cystic Fibrosis
For patients with cystic fibrosis (CF), PFTs are instrumental in tracking disease progression and optimizing airway clearance techniques. Spirometry is commonly used in CF to assess lung function regularly, allowing healthcare providers to detect early signs of decline and tailor treatments accordingly. PFTs also guide the use of medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications related to CF.
Preparing for a Pulmonary Function Test
Before undergoing a PFT, patients may need to refrain from certain medications that could interfere with the test results. Common medications to avoid include bronchodilators, as they can affect airflow measurements. Patients may also be advised to avoid smoking or strenuous exercise before the test, as these activities can temporarily alter lung function. Following these instructions ensures accurate test results, providing healthcare providers with reliable data to inform treatment decisions.
In conclusion…
Pulmonary Function Tests are an invaluable tool in diagnosing, managing, and monitoring respiratory conditions, empowering healthcare providers to offer personalized care and improve patient outcomes. If you have concerns about your lung health or suspect a respiratory condition, don’t hesitate to schedule a PFT at Pulmonary Clinic of the Carolinas. Take charge of your lung health today!


 Translate
Translate