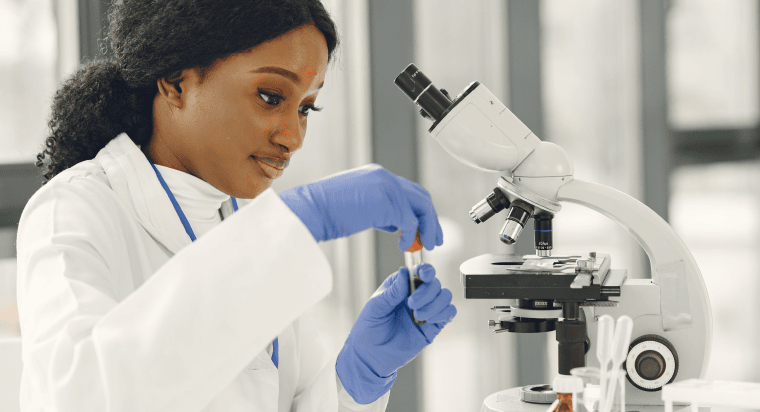
Importance of healthcare screening
In the field of healthcare, early disease detection plays a vital role in improving patient outcomes. Timely identification of diseases at their earliest stages allows for prompt intervention and treatment, increasing the chances of successful recovery. Diagnostic testing is a cornerstone of early detection, enabling healthcare providers to identify potential health issues before they progress. This article will explore the different types of diagnostic testing, the importance of early disease detection, and some common diseases detected through diagnostic testing.
What is Diagnostic Testing?
Before exploring the importance of early disease detection as a benefit of diagnostic testing, it is critical to understand what the term is all about. Diagnostic testing is a crucial component of modern healthcare that involves a range of medical procedures and tests used to identify and diagnose diseases or conditions in patients. The primary objective of diagnostic testing is to gather accurate and relevant information about a patient’s health status, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding treatment plans, interventions, and further investigations.
Diagnostic testing encompasses various techniques and tools that provide valuable insights into the functioning of the human body, from the cellular level to overall organ systems. These tests can be categorized into different types, including laboratory tests, imaging tests, and biopsies.
Types of Diagnostic Testing
There are various types of diagnostic testing depending on the particular needs of an individual. Here are the different types:
1. Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are essential tools in diagnosing various conditions. They include:
- Blood Tests: Blood tests provide valuable insights into a patient’s health. They can measure parameters such as complete blood count, blood sugar levels, cholesterol levels, liver function, and kidney function. Abnormalities in these tests can indicate the presence of underlying health conditions.
- Urine Tests: Urine tests are commonly used to evaluate kidney function and detect urinary tract infections. They can also identify the presence of certain substances in the urine, such as glucose or protein, which may indicate underlying health issues.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing analyzes an individual’s DNA to identify genetic mutations or predispositions to certain diseases. It can help detect inherited disorders, assess the risk of developing certain conditions, and guide personalized treatment plans.
2. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests provide detailed visualizations of internal structures and aid in diagnosing various diseases. They include:
- X-rays: X-rays use low-dose radiation to produce images of bones, organs, and tissues. They are commonly used to detect fractures, tumors, infections, and other abnormalities.
- CT Scans: Computed Tomography (CT) scans utilize multiple X-ray images to create cross-sectional images of the body. They provide detailed information about organs, blood vessels, and soft tissues, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions such as tumors, blood clots, and internal injuries.
- MRI Scans: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans use powerful magnets and radio waves to generate highly detailed images of internal structures. They are particularly useful in evaluating the brain, spinal cord, joints, and soft tissues. MRI scans can detect abnormalities such as tumors, inflammation, and nerve damage.
3. Biopsy
A biopsy involves the collection of tissue samples for microscopic examination. It is commonly performed to diagnose cancers or other conditions that require further investigation at the cellular level. The collected samples are analyzed under a microscope to identify abnormal cellular changes or the presence of cancerous cells. Biopsies are crucial in providing definitive diagnoses for various conditions, particularly cancers and certain autoimmune disorders.
Importance of Early Disease Detection
Having discussed the various types of diagnostic testing, let us consider some of its benefits in promoting positive health.
One of the importance of early disease detection is that it allows for timely intervention and treatment initiation. By identifying diseases in their early stages, healthcare providers can implement appropriate treatment plans, potentially leading to better patient outcomes and an increased likelihood of full recovery.
Early disease detection can lead to significant cost savings in the long run. Timely intervention often requires less extensive treatments or surgeries, reducing healthcare costs for both patients and healthcare systems.
Detecting diseases early enables the identification of risk factors and the implementation of preventive measures. Patients can make necessary lifestyle changes, receive appropriate vaccinations, or undergo prophylactic treatments to reduce the risk of developing certain conditions.
Common Diseases Detected Through Diagnostic Testing
There are several diseases that can be detected through diagnostic testing including cancer and other cardiovascular diseases.
1. Cancer
Regular screenings and diagnostic tests play a crucial role in detecting various types of cancer at early stages. Examples include mammograms for breast cancer, colonoscopies for colorectal cancer, and Pap smears for cervical cancer. Genetic testing can also identify hereditary cancer predispositions.
2. Cardiovascular Diseases
Diagnostic tests such as cholesterol level testing and lipid profile assessments help identify individuals at risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Electrocardiograms (EKGs) and stress tests evaluate heart function and can detect abnormalities that may indicate underlying cardiac conditions.
3. Infectious Diseases
Diagnostic tests are instrumental in detecting infectious diseases, enabling prompt treatment and prevention of their spread. Blood tests can identify infections such as HIV, hepatitis, or sexually transmitted infections. Cultures and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests help identify specific pathogens responsible for infections.
To conclude:
Diagnostic testing plays a pivotal role in early disease detection, allowing healthcare providers to identify potential health issues before they progress. If you have concerns about your health or would like to schedule diagnostic testing, contact the Pulmonary Clinic of the Carolinas today. Our team of experienced healthcare professionals is dedicated to providing early disease detection and personalized care.


 Translate
Translate